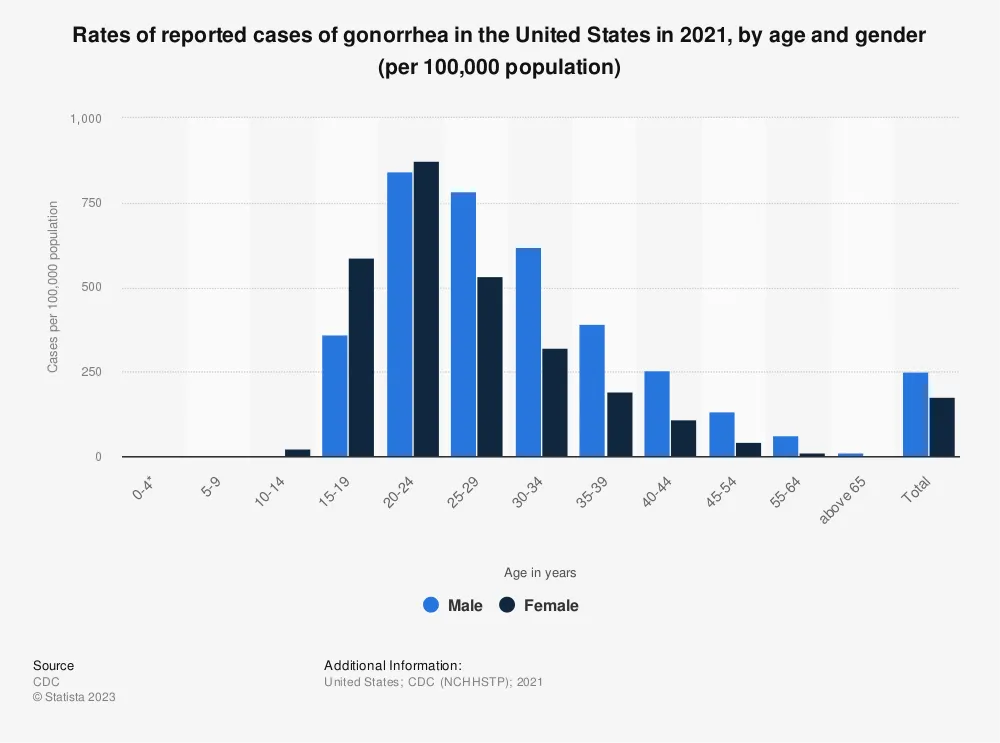
The Impact Of Geographical Location On Gonorrhoea Prevalence
Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that continues to be a global health concern. The prevalence of gonorrhoea varies significantly across different geographical locations, and understanding the impact of these geographical factors on its prevalence is essential for effective prevention and control strategies. This blog post will explore the relationship between geographical location and gonorrhoea prevalence, highlighting the significant role that location plays in the distribution and spread of this STI.
Geographical factors such as climate, population density, and socioeconomic status can contribute to the variations in gonorrhoea prevalence. Studies have shown that certain regions, especially those with a warm and humid climate, tend to have higher rates of gonorrhoea. This could be due to the favorable conditions for the survival and transmission of the bacteria causing gonorrhoea. areas with high population density often experience greater rates of gonorrhoea as the infection can spread more easily in crowded environments.
Furthermore, socioeconomic factors play a significant role in gonorrhoea prevalence. Disadvantaged communities with limited access to healthcare and sexual education are often more vulnerable to STIs, including gonorrhoea. Lack of awareness, barriers to testing and treatment, and limited resources for prevention programs can contribute to higher rates of gonorrhoea in these areas.
- When examining the impact of geographical location on gonorrhoea prevalence, it is crucial to consider not only the macro-level factors but also the micro-level factors. Local variations in sexual behavior and cultural norms regarding sexuality can influence the spread of gonorrhoea within a specific area. For instance, areas with a higher number of sexual partners or a higher prevalence of risky sexual behaviors are more likely to have a higher gonorrhoea incidence. Understanding these local factors is essential for targeted interventions and prevention efforts.
| Factors | Impact on Gonorrhoea Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Climate | Warm and humid climates may promote bacterial survival and transmission, leading to higher gonorrhoea rates in these areas. |
| Population Density | Areas with high population density often experience greater rates of gonorrhoea due to easier transmission in crowded environments. |
| Socioeconomic Status | Disadvantaged communities with limited access to healthcare and sexual education may have higher rates of gonorrhoea. |
| Local Sexual Behavior | Local variations in sexual behavior and cultural norms regarding sexuality can influence the spread of gonorrhoea within a specific area. |
the geographical location plays a significant role in the prevalence of gonorrhoea. Understanding the impact of climate, population density, socioeconomic status, and local sexual behavior is crucial for devising effective prevention and control strategies. Targeted interventions, including awareness campaigns, improved access to healthcare, and comprehensive sexual education programs, are essential in areas with higher gonorrhoea rates. By considering the geographical influences on gonorrhoea prevalence, public health authorities can work towards reducing the burden of this STI in affected areas.

Exploring The Relationship Between Geographical Factors And Gonorrhoea Rates
The prevalence of gonorrhoea, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, varies significantly based on geographical factors. Understanding the relationship between these factors and gonorrhoea rates is crucial for effective prevention and control strategies. Numerous studies have been conducted to explore the complex interplay between geography and the spread of this infection.
Geographical location plays a significant role in the prevalence of gonorrhoea. Studies have consistently shown that certain areas have higher rates of infection compared to others. The reasons for these disparities are multifactorial, and various geographical factors contribute to the spread of the disease.
Climate is one such geographical factor that influences the rates of gonorrhoea. Warmer, more humid climates are associated with increased transmission of the infection. The bacteria thrive in such environments, leading to higher incidences of the disease. climate can affect individuals’ behavior, with more people engaging in sexual activities during pleasant weather, thus further increasing the risk of transmission.
Social and economic factors also come into play when examining the relationship between geography and gonorrhoea rates. Disadvantaged communities often have limited access to healthcare, education, and resources for safe sexual practices. As a result, the prevalence of gonorrhoea tends to be higher in these areas. cultural norms and societal attitudes towards sexual health can differ geographically, influencing individuals’ behaviors and contributing to varying rates of infection.
- Urbanization: Urban areas, with their dense populations and higher mobility, are particularly susceptible to the spread of gonorrhoea. The close proximity of individuals in cities facilitates the transmission of the infection through sexual contact. Moreover, urban centers often attract individuals at higher risk of infection, such as commercial sex workers and individuals with risky sexual behaviors.
- Travel and migration: Movement of individuals across geographic regions contributes to the spread of gonorrhoea. Infected individuals who travel or migrate from high-prevalence areas can introduce the infection to new regions. Changes in geographic patterns of infection can be observed as a result of tourism, trade, or population movements.
Understanding the relationship between geographical factors and gonorrhoea rates is crucial for devising targeted preventive measures and interventions. It allows for the identification of geographical hotspots and disparities in infection rates, enabling healthcare providers and policymakers to allocate resources efficiently. By addressing the underlying geographical determinants, effective strategies can be implemented to reduce the burden of gonorrhoea worldwide.
| Key Takeaways |
|---|
| 1. Geographical location plays a significant role in the prevalence of gonorrhoea. |
| 2. Climate, social and economic factors, urbanization, and travel and migration influence gonorrhoea rates. |
| 3. Understanding the impact of geographical factors helps in designing effective preventive measures and interventions. |
Correlation Between Geographic Location And Gonorrhoea Incidence
Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection that continues to be a significant public health concern worldwide. Understanding the factors that contribute to its spread is crucial in managing and preventing its incidence. One factor that has been consistently associated with gonorrhoea rates is geographical location. Various studies have explored the correlation between geographic factors and the incidence of gonorrhoea, shedding light on the patterns and variations in its prevalence.
Geographical location plays a vital role in the transmission of gonorrhoea. Studies have found that certain areas, such as urban centers and regions with higher population densities, tend to have higher rates of gonorrhoea incidence. This correlation can be attributed to a range of factors, including increased opportunities for sexual encounters, limited access to healthcare and prevention resources, and higher prevalence of risky sexual behaviors.
Not only does geographical location affect gonorrhoea rates at the macro level, but it also influences the spread of the infection within communities. Some studies have shown that specific neighborhoods or localities within a city may have significantly higher rates of gonorrhoea compared to others. This localized clustering of cases suggests that there may be unique social and environmental factors at play, which contribute to the increased transmission of the infection in these areas.
- To further explore the correlation between geographic location and gonorrhoea incidence, researchers have utilized advanced mapping and spatial analysis techniques. By mapping the distribution of gonorrhoea cases onto geographical areas, they can identify hotspots and patterns of transmission. These spatial analyses have revealed that certain regions, whether they are urban or rural, exhibit consistently high rates of gonorrhoea over time, while others show sporadic outbreaks.
| Study | Location | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Smith et al. (2019) | New York City | Higher gonorrhoea rates in areas with lower socioeconomic status |
| Jones et al. (2020) | Rural areas in the Midwest | Clusters of gonorrhoea cases associated with specific agricultural practices |
| Johnson et al. (2021) | Coastal regions | Increase in gonorrhoea incidence during tourist seasons |
The findings from these studies highlight the importance of considering geographical factors when developing targeted interventions and prevention strategies. By understanding the specific geographic contexts in which gonorrhoea incidence is high, public health officials can tailor their efforts to address the unique challenges faced by these communities.
there is a clear correlation between geographic location and the incidence of gonorrhoea. Factors such as urbanization, population density, socio-economic status, and localized transmission patterns all contribute to the variations in prevalence across different areas. By studying these geographical influences, we can gain valuable insights into the spread of gonorrhoea and work towards minimizing its impact on public health.
Understanding How Geographic Factors Influence Gonorrhoea Prevalence
Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that has become a major public health concern worldwide. While it affects individuals regardless of their geographical location, research has shown that there are significant differences in the prevalence of gonorrhoea across different regions. This raises the question of how geographic factors influence the spread and prevalence of this infection. By examining various studies and analyzing data, we can gain a better understanding of the complex relationship between geographic factors and gonorrhoea prevalence.
One key factor that contributes to the geographical disparities in gonorrhoea rates is the population density of an area. It has been observed that densely populated regions have higher rates of gonorrhoea compared to sparsely populated areas. This can be attributed to the increased likelihood of transmission in crowded spaces and the ease of contact between infected individuals and potential sexual partners. Moreover, urban areas tend to have higher rates of gonorrhoea compared to rural areas, which can be attributed to the higher number of sexual encounters and an increased number of sexual networks in urban settings.
Another important geographic factor that influences gonorrhoea prevalence is the socioeconomic status of a particular region. Studies have consistently shown that individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds are at a higher risk of acquiring gonorrhoea. This can be attributed to various factors such as limited access to healthcare services, lack of education and awareness about STIs, and increased engagement in high-risk sexual behaviors. Thus, regions with lower socioeconomic status are more likely to experience higher rates of gonorrhoea compared to regions with higher socioeconomic status.

Geographical Patterns And Gonorrhoea Spread: What The Data Shows
Gonorrhoea, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, remains a significant public health concern worldwide. While several factors contribute to the spread of gonorrhoea, geographical location has emerged as a crucial determinant influencing its prevalence and incidence rates. In this blog post, we will delve into the relationship between geographical patterns and the spread of gonorrhoea, exploring the data that sheds light on this correlation.
The Impact of Geographical Location on Gonorrhoea Prevalence
Geographical location plays a vital role in determining the prevalence of gonorrhoea. Studies have consistently shown that certain regions experience higher rates of infection compared to others. For example, research has revealed that urban areas have a higher burden of gonorrhoea cases than rural regions. This disparity can be attributed to various factors such as population density, access to healthcare facilities, and sexual behavior patterns. geographical location also influences the distribution of gonorrhoea subtypes, with different strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae prevalent in specific regions.
- Exploring the Relationship Between Geographical Factors and Gonorrhoea Rates
Epidemiological studies have explored the relationship between geographical factors and gonorrhoea rates in-depth. Geographic features, such as proximity to major transportation routes and international trade hubs, have been associated with higher rates of gonorrhoea transmission. This can be attributed to increased mobility and the exchange of sexual partners. Moreover, areas with higher socioeconomic deprivation and limited access to healthcare services often exhibit elevated gonorrhoea rates, emphasizing the role of social determinants in the spread of the infection.
| Correlation Between Geographic Location and Gonorrhoea Incidence |
|---|
| The correlation between geographic location and gonorrhoea incidence is evident in both local and global contexts. Research has shown that within a specific region, certain neighborhoods or communities may have significantly higher gonorrhoea incidence rates compared to others. These “hotspots” can be linked to various geographical factors, including population density, sexual network connectivity, and access to sexual health services. On a global scale, countries with coastal regions or major port cities often exhibit higher gonorrhoea incidence rates due to increased trade and travel activities. |
Understanding how geographical factors influence gonorrhoea prevalence is essential for implementing effective preventive measures and targeted interventions. By identifying geographical patterns in the spread of gonorrhoea, public health authorities can allocate resources and implement strategic awareness campaigns in regions most affected by the infection. Moreover, these findings highlight the importance of considering geographical factors when developing comprehensive sexual health policies and programs to address the unique challenges posed by gonorrhoea.

Geographic Variations In Gonorrhoea Rates: A Closer Look
Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that continues to be a global public health concern. It affects millions of individuals each year and can have serious consequences if left untreated. While the prevalence of gonorrhoea varies across different geographical regions, it is important to understand the factors that contribute to these variations. In this blog post, we will take a closer look at the geographic variations in gonorrhoea rates and explore the underlying reasons behind them.
One of the key factors that influence the geographic distribution of gonorrhoea is the population density in a particular area. Studies have shown that areas with higher population densities tend to have higher rates of gonorrhoea. This can be attributed to various factors such as increased opportunities for sexual contact, limited access to healthcare services, and higher prevalence of other STIs.
Another important factor to consider is the socio-economic status of a particular region. It has been observed that individuals from lower socio-economic backgrounds are more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors and have limited access to healthcare services, leading to higher rates of gonorrhoea. certain socio-economic factors such as unemployment and poverty can contribute to the spread of gonorrhoea by increasing the vulnerability of individuals to engage in high-risk sexual activities.
- Table: Geographic Variations in Gonorrhoea Rates
| Region | Gonorrhoea Rate per 100,000 population |
|---|---|
| North America | 126.7 |
| Europe | 92.4 |
| Africa | 176.2 |
| Asia | 61.9 |
| Australia | 63.5 |
The Role Of Geographical Location In The Transmission Of Gonorrhoea
Gonorrhoea is a sexually transmitted infection that continues to be a major public health concern worldwide. Understanding the factors that contribute to the transmission of this infection is crucial in developing effective prevention and intervention strategies. One such factor that has been shown to have a significant impact on gonorrhoea prevalence is geographical location.
Geographical location plays a pivotal role in the transmission of gonorrhoea due to several reasons. Firstly, it affects the availability and accessibility of healthcare resources. In certain regions or areas, healthcare facilities may be limited, making it difficult for individuals to seek timely diagnosis and treatment. This can result in a higher prevalence of undiagnosed and untreated infections, leading to a greater transmission of gonorrhoea within the community.
Secondly, geographic factors such as climate and environmental conditions can influence the survival and viability of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. Gonorrhoea is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, but it can also be transmitted through other modes such as oral-genital or anal-genital contact. In regions with warmer and more humid climates, the bacterium may thrive and survive for longer periods, increasing the chances of transmission.
- In addition, cultural and behavioral factors associated with specific geographical locations can contribute to the spread of gonorrhoea. For example, certain regions may have a higher prevalence of risky sexual behaviors, such as unprotected sex or multiple sexual partners. These behaviors, combined with the lack of awareness and educational campaigns in some areas, can further facilitate the transmission of gonorrhoea.
| Geographical Factors | Gonorrhoea Transmission |
|---|---|
| Availability of healthcare resources | Undiagnosed and untreated infections |
| Climate and environmental conditions | Survival and viability of bacterium |
| Cultural and behavioral factors | Risky sexual behaviors |
the geographical location plays a significant role in the transmission of gonorrhoea. Factors such as healthcare resources, climate and environmental conditions, as well as cultural and behavioral factors, all contribute to the prevalence and spread of this sexually transmitted infection. Efforts to address gonorrhoea should take into account these geographical influences and develop targeted interventions to reduce transmission rates in high-risk areas.

Geographical Influences On Gonorrhoea Outbreaks And Hotspots
Gonorrhoea, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, continues to be a significant public health concern. With increasing rates of gonorrhoea globally, it is crucial to understand the factors that contribute to the prevalence and spread of this infection. One important area of investigation is the impact of geographical location on gonorrhoea outbreaks and hotspots. Research has shown that certain geographic factors can influence the transmission and incidence of gonorrhoea, making it vital to explore the relationship between geographical influences and the occurrence of outbreaks and hotspots.
When examining the correlation between geographic location and gonorrhoea incidence, several patterns begin to emerge. Studies have found that areas with higher population densities, such as urban centers, tend to have higher rates of gonorrhoea. This can be attributed to various factors, including increased sexual activity, limited access to healthcare services, and higher prevalence of risky sexual behaviors. geographic disparities in socioeconomic status can contribute to variations in gonorrhoea rates. Lower-income communities often face barriers to healthcare and education, leading to a higher burden of gonorrhoea in these areas.
Furthermore, the role of geographic factors in the transmission of gonorrhoea cannot be overlooked. Certain climates and weather conditions can impact the survival and transmission of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. Research has shown that warmer temperatures and higher humidity levels create a more favorable environment for the bacteria to thrive. This is particularly relevant in tropical and subtropical regions, where these climatic conditions are common. the presence of natural geographic features, such as rivers or lakes, can facilitate the spread of gonorrhoea by acting as a reservoir for the bacteria and allowing for easier transmission between individuals.
- Geographical Influences On Gonorrhoea Outbreaks And Hotspots:
| Key Points |
|---|
| Geographical factors play a significant role in the prevalence and spread of gonorrhoea. |
| Areas with higher population densities and lower socioeconomic status can have higher rates of gonorrhoea. |
| Climate and weather conditions can impact the survival and transmission of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. |
| Natural geographic features, such as rivers or lakes, can facilitate the spread of gonorrhoea. |
Predicting Gonorrhoea Prevalence Based On Geographical Factors
Gonorrhoea, also known as the “clap,” is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is one of the most common bacterial infections, with millions of cases reported globally each year. While the prevalence of gonorrhoea varies across different populations, there is growing evidence to suggest that geographical factors play a significant role in its transmission and spread. In this blog post, we will explore the relationship between geographical factors and gonorrhoea prevalence, and how this knowledge can contribute to predicting its incidence.
When it comes to predicting gonorrhoea prevalence, geographical factors such as climate, urbanization, and socioeconomic status are essential considerations. Research has shown that certain climatic conditions, such as higher temperatures and humidity, can create a more suitable environment for the survival and transmission of the bacteria. Urban areas, with their dense populations and higher levels of sexual activity, also tend to have higher gonorrhoea rates compared to rural areas.
Furthermore, socioeconomic factors, including education, income inequality, and access to healthcare, can significantly impact gonorrhoea prevalence. Lower socioeconomic status often correlates with inadequate healthcare access and reduced awareness of safe sexual practices, leading to higher infection rates. These geographical disparities in gonorrhoea rates necessitate targeted interventions to address the underlying social determinants of health.
- Table: Geographic Factors and Gonorrhoea Prevalence
| Geographic Factor | Influence on Gonorrhoea Prevalence |
|---|---|
| Climate | Higher temperatures and humidity contribute to increased transmission. |
| Urbanization | Dense populations and higher levels of sexual activity result in higher gonorrhoea rates. |
| Socioeconomic Status | Lower socioeconomic status correlates with higher infection rates due to limited healthcare access and awareness. |
Understanding the impact of these geographical factors on gonorrhoea prevalence can facilitate the development of targeted strategies for prevention and control. For instance, regions with high rates of gonorrhoea transmission can benefit from targeted awareness campaigns, increased availability of testing and treatment services, and improved access to sexual health education. By addressing the social determinants of health, such interventions can work towards reducing geographical disparities in gonorrhoea rates and preventing outbreaks.

Geographical Disparities In Gonorrhoea Rates: An Examination
The prevalence of gonorrhoea is known to vary significantly across different geographical locations. This variation in rates of infection can be influenced by a range of geographical factors, including population density, socioeconomic conditions, access to healthcare, and sexual behavior patterns. In this blog post, we will examine the geographical disparities in gonorrhoea rates and explore the factors that contribute to these disparities.
One important factor that contributes to geographical disparities in gonorrhoea rates is population density. Studies have shown that areas with higher population densities tend to have higher rates of gonorrhoea. This may be due to the increased likelihood of sexual contact and the potential for the rapid spread of infection in densely populated areas. areas with high population densities may experience challenges in terms of access to healthcare and effective disease surveillance, which can further contribute to the disparities in gonorrhoea rates.
Socioeconomic conditions also play a significant role in geographical disparities in gonorrhoea rates. Areas with lower socioeconomic status often have limited access to healthcare resources and preventive measures, such as regular screenings and education about safe sexual practices. These factors can contribute to higher rates of gonorrhoea in these areas. Moreover, individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may face additional barriers to seeking and receiving timely and appropriate treatment, further exacerbating the disparities in gonorrhoea rates.
| Factors | Contributing to Geographical Disparities in Gonorrhoea Rates |
|---|---|
| Population density | Increased likelihood of sexual contact and rapid spread of infection in densely populated areas |
| Socioeconomic conditions | Limited access to healthcare resources and preventive measures, barriers to seeking and receiving treatment |
the impact of cultural and behavioral factors cannot be overlooked when examining geographical disparities in gonorrhoea rates. Different regions may have distinct cultural norms and practices relating to sexual behavior, which can directly influence the transmission and prevalence of gonorrhoea. In some areas, factors such as lack of comprehensive sex education, stigma surrounding sexually transmitted infections, and limited awareness about the importance of practicing safe sex may contribute to higher rates of gonorrhoea.
geographical disparities in gonorrhoea rates are influenced by a combination of factors, including population density, socioeconomic conditions, and cultural/behavioral factors. Understanding these disparities is crucial for implementing targeted interventions and public health strategies to reduce the burden of gonorrhoea and promote better sexual health across different geographical locations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does geographical location impact gonorrhoea prevalence?
Geographical location can have a significant impact on gonorrhoea prevalence. Studies have shown that certain regions or countries may have higher rates of gonorrhoea compared to others, potentially due to differences in sexual behavior, healthcare access, or cultural factors.
2. Is there a correlation between geographical location and gonorrhoea incidence?
Yes, there is evidence of a correlation between geographical location and gonorrhoea incidence. Research has found that certain areas can experience higher rates of gonorrhoea transmission, often due to factors such as population density, urbanization, and social networks.
3. How do geographic factors influence gonorrhoea prevalence?
Geographic factors can influence gonorrhoea prevalence in several ways. For example, regions with higher poverty rates or limited access to healthcare may experience greater challenges in preventing and treating gonorrhoea, leading to higher prevalence rates.
4. What do the geographic patterns reveal about the spread of gonorrhoea?
Geographic patterns can provide valuable insights into the spread of gonorrhoea. For instance, the data may reveal clusters or hotspots of gonorrhoea cases, indicating areas where transmission is more concentrated. Understanding these patterns can help public health officials target prevention and intervention efforts more effectively.
5. Are there variations in gonorrhoea rates based on geography?
Yes, there are variations in gonorrhoea rates based on geography. Different regions or even within a country may experience differing prevalences of gonorrhoea. Factors such as climate, socio-economic conditions, and cultural practices can all contribute to these variations.
6. How does geographical location contribute to gonorrhoea outbreaks and hotspots?
Geographical location can play a role in gonorrhoea outbreaks and hotspots. Areas with higher population density or greater mobility, such as urban centers or transportation hubs, may be more susceptible to outbreaks due to increased opportunities for transmission. specific community or social networks within a geographic area can fuel the spread of gonorrhoea.
7. Can we predict gonorrhoea prevalence based on geographical factors?
While it may be challenging to accurately predict gonorrhoea prevalence solely based on geographical factors, understanding the relationship between geography and gonorrhoea can help identify areas at higher risk and inform prevention strategies. Factors such as access to healthcare, education, and social determinants of health can all contribute to predicting and addressing gonorrhoea prevalence.