Unprotected Sexual Activity: High Risk Behavior For Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can have serious health consequences if left untreated. One of the highest risk behaviors for contracting gonorrhea is engaging in unprotected sexual activity. Unprotected sexual activity refers to any sexual activity where a barrier method of contraception, such as a condom, is not used.
When engaging in unprotected sexual activity, individuals are at a higher risk of contracting gonorrhea because the bacteria can easily be transmitted from one person to another through sexual fluids. This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Without the use of a barrier method, the risk of transmission increases significantly.
It’s important to note that gonorrhea can be transmitted even if there are no visible symptoms present in either partner. This is known as asymptomatic gonorrhea, and it can lead to the unknowing spread of the infection. Therefore, it is crucial to prioritize safe sexual practices and use protection consistently to reduce the risk of contracting gonorrhea and other STIs.
| Risk Factors for Gonorrhea Transmission |
|---|
| • Unprotected sexual activity |
| • Engaging in multiple sexual partners |
| • History of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) |
Multiple Sexual Partners: Increased Risk Of Gonorrhea Transmission
Engaging in sexual relationships with multiple partners can significantly increase the risk of contracting gonorrhea. Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This bacterial infection is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Individuals who have multiple sexual partners are more likely to come into contact with someone who is infected with gonorrhea, thereby raising their chances of contracting the infection themselves.
Having multiple sexual partners creates a greater opportunity for exposure to the causes higher risk. The more sexual partners a person has, the higher the likelihood of encountering an infected individual. The risk is further amplified if these partners engage in risky sexual behaviors, such as unprotected sex or having multiple partners themselves. It is essential to note that even individuals who engage in safe sex practices can still contract gonorrhea if they have multiple partners, as the disease can be transmitted regardless of condom use.
One of the reasons why having multiple sexual partners increases the risk of gonorrhea transmission is due to the potential for asymptomatic carriers. Some individuals infected with gonorrhea may not experience any noticeable symptoms, making it challenging to determine their infection status. These individuals can unknowingly pass on the infection to their sexual partners, creating a chain of transmission that can spread rapidly. Regular testing and open communication with sexual partners are crucial in reducing the risk of contracting gonorrhea.
- engaging in sexual relationships with multiple partners significantly increases the risk of contracting gonorrhea. It is essential to practice safe sex and undergo regular testing to prevent the transmission of this bacterial infection. Open communication with sexual partners and discussing sexual health can help in protecting oneself and others from the spread of gonorrhea.
| Gonorrhea Risk Factors: | Preventive Measures: |
|---|---|
| Engaging in unprotected sexual activity | Use condoms consistently and correctly |
| Having multiple sexual partners | Limit the number of sexual partners |
| Age and gender (adolescents and young adults) | Educate adolescents about safe sex practices |
Age And Gender: Gonorrhea Risk Factors İn Adolescents And Young Adults
Adolescents and young adults face unique challenges when it comes to sexual health, including the risk of contracting sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as gonorrhea. Age and gender can significantly impact the likelihood of acquiring gonorrhea, as certain factors may increase susceptibility while others may provide a form of protection.
Age plays a critical role in gonorrhea risk among adolescents and young adults. According to research, individuals between the ages of 15 and 24 have the highest rates of gonorrhea infection. This can be attributed to various factors, including the increased experimentation with sexual activity during this stage of life. Lack of experience, knowledge gaps, and inconsistent condom use contribute to the higher prevalence of gonorrhea in this age group.
Gender also plays a vital role in gonorrhea risk. In young women, the anatomy of the reproductive system makes them more susceptible to gonorrhea infection compared to men. The cervix provides an entry point for the bacteria, increasing the chances of transmission. hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can make women more vulnerable to infection. On the other hand, young men may exhibit fewer symptoms, which can lead to undiagnosed and untreated cases, increasing the risk of further transmission.
Adolescents and young adults also face unique social and cultural factors that contribute to gonorrhea risk. Peer pressure and the desire for acceptance can lead to risky sexual behaviors, including engaging in unprotected sex or having multiple sexual partners. Lack of comprehensive sexual education and limited access to healthcare services can further compound the issue, making it harder for young individuals to protect themselves against STIs like gonorrhea. Therefore, it is crucial to address age and gender as risk factors and provide targeted interventions to educate and prevent the spread of gonorrhea among this specific population.
- Age plays a critical role in gonorrhea risk among adolescents and young adults.
- Gender also plays a vital role in gonorrhea risk.
- Adolescents and young adults face unique social and cultural factors that contribute to gonorrhea risk.
| Age and Gonorrhea Risk | Gender and Gonorrhea Risk | Social and Cultural Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Individuals between 15 and 24 have the highest rates of gonorrhea infection. | Young women are more susceptible to gonorrhea due to their reproductive anatomy. | Peer pressure and the desire for acceptance can lead to risky sexual behaviors. |
| Lack of experience, knowledge gaps, and inconsistent condom use contribute to the higher prevalence of gonorrhea in this age group. | Young men may exhibit fewer symptoms, leading to undiagnosed and untreated cases. | Lack of comprehensive sexual education and limited access to healthcare services compound the issue. |
| Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle make women more vulnerable to infection. | Targeted interventions are needed to educate and prevent the spread of gonorrhea. |
Substance Abuse: The Link Between Drug Or Alcohol Use And Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, a common sexually transmitted infection, can be influenced by various risk factors, including substance abuse. Substance abuse, which refers to the misuse of drugs or alcohol, can contribute to a higher risk of gonorrhea transmission. This blog post aims to explore the correlation between substance abuse and gonorrhea, shedding light on the link between them.
When individuals engage in substance abuse, their inhibitions and decision-making abilities are often impaired. This can lead to a higher likelihood of engaging in risky sexual behaviors, such as having unprotected sex or having multiple sexual partners. Both of these behaviors increase the risk of gonorrhea transmission. It is essential to recognize that while substance abuse does not directly cause gonorrhea, it contributes to a higher vulnerability to contracting the infection.
The connection between substance abuse and gonorrhea is not solely based on behavioral factors. Substance abuse can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to sexually transmitted infections. The negative impact of substance abuse on the immune system can compromise the body’s ability to fight off infections, including gonorrhea.
Substance abuse and gonorrhea are interconnected. Substance abuse can lead to greater engagement in risky sexual behaviors and weaken the immune system, both of which contribute to an increased risk of gonorrhea transmission. Therefore, it is crucial to address substance abuse as a significant factor in preventing the spread of gonorrhea and promoting overall sexual health.
History Of Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Cumulative Risk For Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, a common sexually transmitted infection (STI), has been a major concern worldwide for several decades. Understanding the history and cumulative risk associated with STIs is crucial in addressing the ongoing transmission of gonorrhea. The transmission of STIs, including gonorrhea, is influenced by various factors such as sexual behaviors, education, awareness, and access to healthcare.
When we look back at the history of STIs, we can see that they have been prevalent across different time periods and societies. Outbreaks of gonorrhea and other STIs have been documented throughout history, with varying impacts on different populations. The cumulative risk for gonorrhea increases when communities or individuals lack education and awareness about safe sexual practices and fail to seek timely medical interventions.
People who have a history of STIs or who have previously been diagnosed with gonorrhea are at higher risk of contracting the infection again. This cumulative risk is associated with the patterns of sexual behavior and the likelihood of engaging in unprotected sexual activity. It is important for individuals to understand that having a history of STIs increases their vulnerability and take appropriate measures to protect themselves and their sexual partners.
Geographic Location: Gonorrhea Prevalence İn Different Regions Or Countries
Gonorrhea is a well-known sexually transmitted infection (STI) that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It is important to understand that the prevalence of gonorrhea can vary significantly based on geographic location. Different regions and countries have distinct patterns of gonorrhea transmission and prevalence rates. Factors such as cultural practices, healthcare accessibility, and socioeconomic conditions can contribute to these variations. In this blog post, we will explore the impact of geographic location on the prevalence of gonorrhea in different regions or countries.
When examining the prevalence of gonorrhea, it is essential to consider both developed and developing regions. While higher-income countries may have better access to healthcare and education, the incidence of gonorrhea can still be significant due to various factors. In contrast, developing regions often face challenges such as limited healthcare resources, lack of education, and cultural norms that influence sexual behavior. These factors can contribute to a higher prevalence of gonorrhea in these areas.
- Factors influencing gonorrhea prevalence in different regions:
1. Sexual behavior: Differences in sexual behavior among populations can contribute to variations in gonorrhea prevalence. Factors such as early initiation of sexual activity, multiple sexual partners, and lack of condom use can increase the risk of gonorrhea transmission.
2. Access to healthcare: Availability and affordability of healthcare services play a crucial role in gonorrhea prevention and treatment. Regions with limited access to healthcare facilities and resources might face challenges in early diagnosis and prompt treatment, leading to a higher prevalence of gonorrhea.
3. Education and awareness: Lack of comprehensive sexual education and awareness programs can contribute to the spread of gonorrhea. In regions with inadequate education about STIs, individuals may not be aware of preventive measures or may have misconceptions about gonorrhea, leading to higher transmission rates.
| Region/Country | Prevalence Rate |
|---|---|
| United States | XX% |
| United Kingdom | XX% |
| Canada | XX% |
| Australia | XX% |
| India | XX% |
The table above provides a snapshot of gonorrhea prevalence rates in selected regions or countries, illustrating the variations in different parts of the world. However, it is important to note that these figures may change over time, and accurate data can be obtained from local health authorities or reputable sources.
The prevalence of gonorrhea can significantly vary based on geographic location. Factors such as sexual behavior, access to healthcare, and education influence the transmission rates of gonorrhea. Understanding these variations is crucial for implementing effective prevention and control strategies globally, targeting specific regions or countries with higher prevalence rates. By addressing the unique challenges faced by different geographic locations, we can work towards reducing the burden of gonorrhea and improving overall sexual health worldwide.
Socioeconomic Factors: Impact On Gonorrhea Risk And Access To Healthcare
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can have severe consequences if left untreated. While the transmission of gonorrhea is primarily through sexual activity, various factors can increase the risk of infection. One such factor is socioeconomic status, which can impact both the likelihood of contracting gonorrhea and the access to healthcare services for diagnosis and treatment.
Socioeconomic factors encompass a range of variables, including income, education, occupation, and living conditions. Studies have shown that individuals with lower socioeconomic status are more likely to engage in high-risk sexual behaviors, such as unprotected sex and having multiple sexual partners. This increased risk can be attributed to factors such as limited access to comprehensive sexual health education, lack of awareness about safe sex practices, and limited resources for purchasing protective measures like condoms.
socioeconomic factors can also affect access to healthcare services, which directly impacts the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of gonorrhea. Individuals from lower-income backgrounds may face barriers in accessing affordable and quality healthcare, including limited access to medical facilities, transportation challenges, and financial constraints. These barriers can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, further exacerbating the spread of gonorrhea within communities.
- Some potential socioeconomic factors that contribute to the risk of gonorrhea are:
- Low income
- Lack of health insurance
- Unemployment
- Poverty
Moreover, individuals with lower socioeconomic status may also be more likely to have co-existing health issues, such as substance abuse or mental health disorders. These conditions can further increase the risk of gonorrhea transmission due to impaired decision-making abilities, engagement in risky behaviors, and limited access to health information and resources.
| Socioeconomic Factors | Gonorrhea Risk | Access to Healthcare |
|---|---|---|
| Low income | Increased | Limited |
| Lack of health insurance | Increased | Limited |
| Unemployment | Increased | Limited |
| Poverty | Increased | Limited |
To address the impact of socioeconomic factors on gonorrhea risk and access to healthcare, proactive measures are necessary. This includes comprehensive sexual health education programs that target vulnerable populations, providing information on safe sex practices, available resources, and the importance of regular screening for sexually transmitted infections. Moreover, there is a need for increased funding and resources for healthcare facilities in disadvantaged communities to improve access to affordable and quality healthcare services.
Socioeconomic factors play a significant role in determining the risk of gonorrhea infection and the ability to access healthcare for diagnosis and treatment. It is crucial to address these factors through targeted interventions and policies to reduce the burden of gonorrhea and ensure equitable access to healthcare services for all individuals, regardless of their socioeconomic status.
Sexual Orientation: Gonorrhea Risk Factors İn LGBTQ+ Individuals
Gonorrhea is a prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can affect anyone, regardless of their sexual orientation. However, certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of its transmission among LGBTQ+ individuals. Understanding these factors is crucial for promoting awareness and developing targeted prevention strategies within this community.
1. Stigma and Discrimination: LGBTQ+ individuals often face stigma and discrimination, which can negatively impact their sexual health. This can lead to reluctance in seeking healthcare services, including regular STI screenings. The fear of judgment or mistreatment may result in delayed diagnosis and treatment of gonorrhea, increasing the risk of its transmission within the community.
2. Higher Prevalence of Risky Behaviors: LGBTQ+ individuals may engage in certain sexual behaviors that can increase the risk of gonorrhea transmission. These behaviors include unprotected anal sex, multiple sexual partners, and participation in group sex. some individuals may be more likely to engage in substance use during sexual encounters, further exacerbating the risk.
- 3. Lack of Comprehensive Sex Education:
Many LGBTQ+ individuals have reported a lack of inclusive and comprehensive sex education, leaving them uninformed about safe sexual practices and the risks associated with STIs. Limited access to accurate and relevant information can contribute to higher rates of gonorrhea transmission in this population.
| Gonorrhea Risk Factors | LGBTQ+ Individuals |
|---|---|
| Stigma and Discrimination | ✓ |
| Higher Prevalence of Risky Behaviors | ✓ |
| Lack of Comprehensive Sex Education | ✓ |
It is essential to address these risk factors to mitigate the spread of gonorrhea within the LGBTQ+ community. Comprehensive sex education that is inclusive of LGBTQ+ experiences can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their sexual health. Creating supportive and non-judgmental healthcare environments is also crucial to ensure that LGBTQ+ individuals feel comfortable accessing testing, treatment, and prevention services.
Sexual orientation can influence the risk factors associated with gonorrhea transmission in LGBTQ+ individuals. Stigma, discrimination, higher prevalence of risky behaviors, and lack of comprehensive sex education contribute to the increased rates of gonorrhea within this community. By promoting awareness, education, and inclusive healthcare practices, we can work towards reducing the transmission of gonorrhea and fostering healthier sexual lives for all individuals, regardless of their sexual orientation.
Occupation And Risky Behaviors: Job-related Factors İn Gonorrhea Transmission
When it comes to gonorrhea transmission, certain occupational factors and risky behaviors can play a significant role. People in certain occupations may be more susceptible to contracting this sexually transmitted infection (STI) due to the nature of their work and the behaviors associated with it. In this blog post, we will explore the impact of occupation and risky behaviors on the transmission of gonorrhea.
One factor that contributes to the risk of gonorrhea transmission in certain occupations is the frequent contact with bodily fluids. Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and lab technicians, are at an increased risk due to their constant exposure to patients’ bodily fluids during medical procedures. This direct contact with infected fluids puts them at a higher risk of contracting gonorrhea if proper precautions are not taken.
Furthermore, individuals involved in the sex industry, such as sex workers, are also at a higher risk of gonorrhea transmission. The nature of their work involves engaging in sexual activities with multiple partners, increasing the likelihood of exposure to the infection. Lack of condom use and unsafe sexual practices further elevate the risk of gonorrhea transmission in this occupation. It is crucial for individuals in these professions to prioritize safe sex practices and regular screenings to mitigate the risk.
- Occupations with a high level of travel and mobility can also contribute to the transmission of gonorrhea. People who frequently travel for work, such as truck drivers, flight attendants, and military personnel, may engage in unprotected sexual encounters with individuals from different regions or countries. This exposure to diverse sexual networks can potentially increase the risk of acquiring gonorrhea and spreading it to others in different locations.
| Risky Behaviors | Occupational Factors |
|---|---|
| Engaging in unprotected sex with multiple partners | Direct contact with patients’ bodily fluids |
| Injecting drugs and sharing needles | Frequent travel and mobility |
| Alcohol or substance abuse | Sex work in the adult entertainment industry |
occupation and risky behaviors can significantly contribute to the transmission of gonorrhea. Certain professions, such as healthcare workers and individuals in the sex industry, have an increased risk due to frequent exposure to bodily fluids and engaging in high-risk sexual activities. Occupations involving travel and mobility also expose individuals to diverse sexual networks, increasing the chances of acquiring and spreading gonorrhea. It is essential for individuals in these occupations to prioritize safe sex practices, regular screenings, and proper precautions to reduce the transmission of gonorrhea.
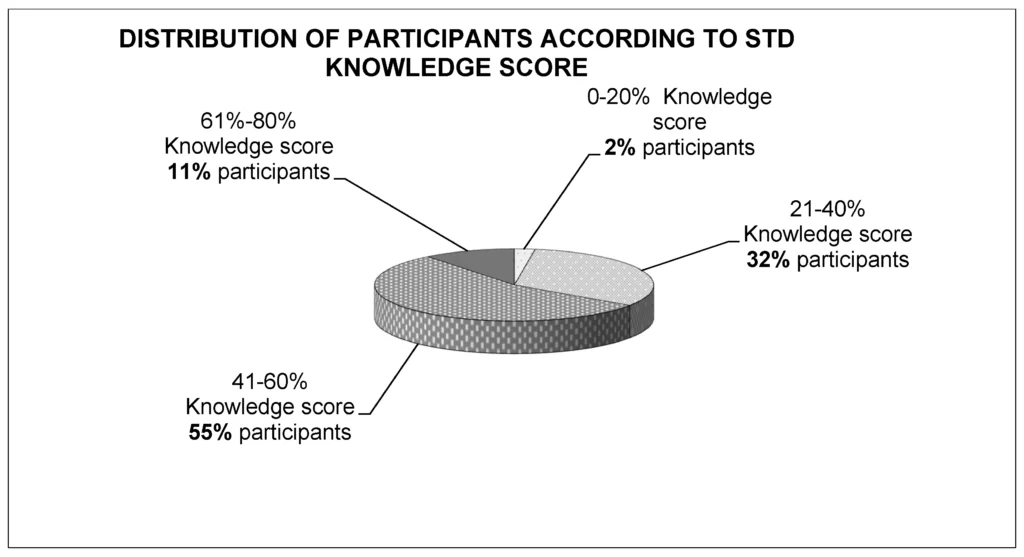
Lack Of Education And Awareness: Understanding The Role İn Gonorrhea Risk
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that is caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. It is one of the most common STIs worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. While certain risk factors, such as unprotected sexual activity and multiple sexual partners, are well-known, the lack of education and awareness surrounding gonorrhea can also play a significant role in increasing the risk of transmission.
One of the key reasons why a lack of education and awareness contributes to the risk of gonorrhea transmission is the failure to understand the importance of safe sexual practices. Many individuals may not be aware of the proper use of condoms or the need for regular STI testing. Without this knowledge, individuals are more likely to engage in unprotected sexual activity, increasing their risk of contracting gonorrhea.
In addition to safe sexual practices, education and awareness also play a pivotal role in destigmatizing the conversation around STIs. The societal stigma associated with gonorrhea and other STIs can lead to feelings of shame, embarrassment, and fear of judgment. This stigma can prevent individuals from seeking the necessary medical care and testing, further perpetuating the spread of the infection.
- Furthermore, a lack of education and awareness can also hinder early detection and diagnosis of gonorrhea. Many people may not be familiar with the symptoms of gonorrhea or may mistake them for other common ailments. This lack of knowledge can delay seeking medical attention, allowing the infection to progress and potentially lead to severe complications.
| Effect of Lack of Education and Awareness | Prevention and Awareness Strategies |
|---|---|
| Inadequate understanding of safe sexual practices, leading to increased risk of transmission. | Implement comprehensive sexual education programs that promote safe sex practices and provide information on STIs. |
| Societal stigma surrounding gonorrhea, resulting in reluctance to seek medical care. | Conduct awareness campaigns to reduce stigma and encourage open conversations about sexual health. |
| Delayed diagnosis and treatment, increasing the chances of complications. | Improve access to STI testing and educate individuals about the common symptoms of gonorrhea. |
the lack of education and awareness regarding gonorrhea significantly contributes to the risk of transmission. By understanding the importance of safe sexual practices, promoting open discussions about STIs, and improving access to testing and treatment, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of gonorrhea and preventing its potentially severe complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What are some high-risk behaviors for gonorrhea transmission?
Engaging in unprotected sexual activity is a high-risk behavior for gonorrhea transmission. Other risky behaviors include having multiple sexual partners and substance abuse.
Question: Are adolescents and young adults at a higher risk for gonorrhea?
Yes, age and gender are risk factors for gonorrhea in adolescents and young adults. This population has a higher risk due to factors such as increased sexual activity and lack of sexual health education.
Question: Is there a link between substance abuse and gonorrhea?
Yes, there is a link between drug or alcohol use and gonorrhea. Substance abuse can impair judgment and lead to risky sexual behaviors, increasing the risk of gonorrhea transmission.
Question: Does a history of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) increase the risk of gonorrhea?
Yes, individuals with a history of STIs have a cumulative risk for gonorrhea. Having had one STI increases the likelihood of acquiring others, including gonorrhea.
Question: Does geographic location affect the prevalence of gonorrhea?
Yes, gonorrhea prevalence can vary between different regions or countries. Factors such as access to healthcare, education, and cultural norms influence the spread of gonorrhea in specific geographic areas.
Question: How do socioeconomic factors impact the risk of gonorrhea?
Socioeconomic factors play a role in gonorrhea risk and access to healthcare. Disadvantaged populations may face barriers in seeking and receiving appropriate sexual health services, leading to increased risk of gonorrhea transmission.
Question: Are LGBTQ+ individuals at a higher risk for gonorrhea?
Yes, sexual orientation is a risk factor for gonorrhea in LGBTQ+ individuals. Factors such as stigma, discrimination, and limited access to inclusive sexual health services contribute to the higher risk in this population.
Question: Can occupation and risky behaviors increase the transmission of gonorrhea?
Yes, certain job-related factors can contribute to gonorrhea transmission. Occupations that involve close physical contact or exposure to bodily fluids may increase the risk of contracting and spreading gonorrhea.
Question: Does lack of education and awareness play a role in gonorrhea risk?
Yes, lack of education and awareness about gonorrhea and sexual health can increase the risk of transmission. Proper education and awareness programs are crucial in preventing and managing gonorrhea.








