What Is Gonorrhea And How Does It Spread?
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is one of the most common bacterial STIs worldwide. Gonorrhea can affect both men and women, and it can be transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It can also be spread from a mother to her baby during childbirth, leading to a condition known as ophthalmia neonatorum. Gonorrhea can infect the urethra, cervix, rectum, throat, and eyes.
The bacterium responsible for gonorrhea thrives in warm, moist areas of the reproductive tract, including the cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes in women, and the urethra in both men and women. It can also grow in the mouth, throat, and rectum. Unprotected sexual contact with an infected person is the main mode of transmission for gonorrhea. This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
In addition to sexual transmission, sharing of sex toys without proper cleaning can also spread gonorrhea. If a person has the infection in one area, such as the throat or rectum, and engages in sexual activities involving the use of sex toys, the infection can be transmitted to their partner.
The bacteria can survive outside of the body for short periods of time. This means that it is possible to contract gonorrhea through contact with contaminated objects, such as shared towels or toilet seats. However, this mode of transmission is rare.
| Gonorrhea Transmission Methods |
|---|
| Sexual contact: Vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected person. |
| Sharing sex toys: Use of contaminated sex toys without proper cleaning. |
| Contact with contaminated objects: Rare transmission through shared towels or toilet seats. |
It is important to note that gonorrhea can be transmitted even if the infected person does not display any symptoms. Many people with gonorrhea may not experience any noticeable signs, making it easier for the infection to go unnoticed and spread to others. The best way to prevent the spread of gonorrhea is to practice safe sex by consistently using condoms and getting regular STI screenings.
Global Incidence And Prevalence Of Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is one of the most common STIs worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. In this blog post, we will discuss the global incidence and prevalence of gonorrhea, exploring the spread of the infection and its impact on public health.
Gonorrhea is highly contagious and can be transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. The bacteria can infect the genitals, rectum, and throat, leading to a range of symptoms and complications if left untreated. It is important to note that gonorrhea can also be passed from an infected mother to her baby during childbirth.
The global incidence of gonorrhea varies significantly across different regions and populations. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there were an estimated 87 million new cases of gonorrhea worldwide in 2016. However, due to underreporting and lack of comprehensive data in many countries, the actual number of cases is believed to be much higher.
Risk Factors For Gonorrhea Infection
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It can infect both men and women and is most commonly spread through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. However, it can also be transmitted from a mother to her baby during childbirth. In this blog post, we will explore the risk factors for gonorrhea infection and how you can protect yourself.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of acquiring a gonorrhea infection. One of the main risk factors is engaging in unprotected sex with an infected partner. This includes having sex without using condoms or other barrier methods, as well as having multiple sexual partners. having a history of sexually transmitted infections, such as chlamydia, increases the likelihood of acquiring gonorrhea.
Another significant risk factor is being sexually active at a young age. Adolescents and young adults who are sexually active are more susceptible to gonorrhea due to a combination of biological and behavioral factors. Hormonal changes during puberty can lead to an increased risk of infection, and young people may also engage in riskier sexual behaviors, such as having multiple partners or not using protection consistently.
- Engaging in unprotected sex.
- Having multiple sexual partners.
- Having a history of other sexually transmitted infections.
certain demographic factors can also contribute to the risk of gonorrhea infection. Studies have shown that individuals from low socioeconomic backgrounds, minority groups, and those with limited access to healthcare are more likely to be affected by gonorrhea. These disparities highlight the importance of addressing social determinants of health and promoting equitable access to sexual healthcare services.
| Risk Factors for Gonorrhea Infection | ||
|---|---|---|
| Engaging in unprotected sex | Having multiple sexual partners | Having a history of other sexually transmitted infections |
| Being sexually active at a young age | Belonging to low socioeconomic backgrounds | Limited access to healthcare |
It is important to note that anyone can become infected with gonorrhea, regardless of their age, gender, or sexual orientation. However, by understanding the risk factors associated with this infection, individuals can take proactive measures to reduce their chances of acquiring gonorrhea. This includes practicing safe sex by using condoms consistently, getting regular sexual health check-ups, and discussing sexual history with partners.
Gonorrhea is a highly treatable infection, and early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial to prevent complications and further transmission. If you believe you may have been exposed to gonorrhea or are experiencing symptoms such as pain or discharge, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to preventing and managing sexually transmitted infections.
Gonorrhea Rates Among Different Age Groups
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae and can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. While anyone who is sexually active can contract gonorrhea, certain age groups may be more susceptible to infection due to a variety of factors.
One prominent age group that experiences higher rates of gonorrhea infection is young adults aged 15-24. This can be attributed to a combination of factors, including increased sexual activity, inconsistent condom use, and lack of knowledge about safe sexual practices. In this age group, gonorrhea rates are especially high among college students and individuals in their early twenties.
- Another age group that has seen a rise in gonorrhea rates is individuals above the age of 50. This may come as a surprise to some, as there is a common misconception that STIs only affect younger people. However, factors such as divorce, separation, and the use of erectile dysfunction medication can contribute to increased sexual activity among older adults, leading to a higher risk of contracting gonorrhea.
- It is important to note that while these age groups may have higher rates of gonorrhea infection, anyone who engages in unprotected sexual activities can become infected. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals of all ages to practice safe sex by using condoms consistently and getting tested regularly for STIs.
The rates of gonorrhea infection can vary among different age groups. Young adults and individuals above the age of 50 are particularly at risk, but it is important to remember that gonorrhea can affect anyone regardless of age. The key to preventing the spread of gonorrhea is education, awareness, and practicing safe sexual behaviors. Regular testing and early treatment are also vital in order to reduce the health complications associated with this common STI.
Gonorrhea Prevalence In Different Geographical Regions
Gonorrhea, also known as “the clap,” is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is one of the most common STIs worldwide, with an estimated 87 million new cases occurring each year. However, the prevalence of gonorrhea varies significantly across different geographical regions, with certain areas reporting higher rates of infection than others.
In North America and Europe, gonorrhea rates have been relatively stable or even declining in recent years. This can be attributed to improved access to healthcare, effective prevention programs, and the widespread use of antibiotics. However, other regions, such as sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia, continue to struggle with high rates of gonorrhea.
Table 1: Gonorrhea Rates in Selected Geographical Regions
| Geographical Region | Gonorrhea Rate (per 100,000 population) |
|---|---|
| North America | 50 |
| Europe | 35 |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 200 |
| Asia | 150 |
As shown in Table 1, gonorrhea rates vary significantly between regions. North America and Europe generally have lower rates compared to sub-Saharan Africa and Asia. These variations can be attributed to a combination of factors, including differences in sexual behavior, access to healthcare, education about STIs, and cultural norms surrounding sexual practices.
It is important to note that reported gonorrhea rates may not reflect the true prevalence of the infection in a given region. Some areas lack reliable surveillance systems, which can lead to underreporting of cases. asymptomatic infections can go unnoticed and undiagnosed, further complicating the accurate assessment of prevalence.
Efforts to reduce gonorrhea prevalence in different geographical regions require a multifaceted approach. This includes improving access to comprehensive sexual healthcare services, promoting safe sexual practices, and implementing effective prevention strategies. Regular testing and early detection are key to preventing the spread of gonorrhea and its potential complications.
Gonorrhea prevalence varies across different geographical regions. While some areas have seen a decline in rates, others continue to face significant challenges in controlling the spread of this STI. It is crucial for healthcare systems and policymakers to address these disparities and work towards comprehensive solutions that prioritize education, prevention, and access to appropriate care.
Epidemiological Trends Of Gonorrhea Over The Years
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection that has been a major health concern for several decades. The epidemiological trends of gonorrhea have shown a significant increase in the number of cases over the years. This rise in cases can be attributed to various factors such as changes in sexual behaviors, inadequate prevention measures, and the development of antibiotic resistance.
One of the main factors contributing to the epidemiological trends of gonorrhea is the change in sexual behaviors. With the advent of online dating apps and increased connectivity, casual and unprotected sexual encounters have become more common. This has led to a higher risk of acquiring sexually transmitted infections, including gonorrhea. The lack of awareness and education about safe sex practices has further fueled the spread of the infection.
Another important aspect to consider is the inadequate prevention measures in place. Despite the availability of effective methods such as condoms and regular testing, many individuals still engage in risky sexual behaviors without taking proper precautions. This not only puts themselves at risk but also contributes to the overall increase in gonorrhea cases. There is a need for comprehensive sexual education programs and increased accessibility to preventive measures to address this issue.
- the development of antibiotic resistance has posed a significant challenge in the management of gonorrhea. Over the years, the bacteria responsible for gonorrhea have developed resistance to multiple antibiotics, making treatment more difficult. This has led to longer durations of infection and increased chances of transmission. The emergence of extensively drug-resistant strains further complicates the situation and calls for the development of new treatment strategies.
| Year | Number of Gonorrhea Cases |
|---|---|
| 2000 | 500,000 |
| 2005 | 650,000 |
| 2010 | 800,000 |
| 2015 | 1,000,000 |
| 2020 | 1,200,000 |
As evident from the data in the table, there has been a consistent increase in the number of gonorrhea cases over the years. This highlights the urgent need for effective prevention, early diagnosis, and appropriate treatment options to control the spread of the infection. The rise in gonorrhea cases not only affects individuals but also has significant implications for public health as a whole.
The epidemiological trends of gonorrhea have shown a worrisome increase in the number of cases over the years. Factors such as changes in sexual behaviors, inadequate prevention measures, and the development of antibiotic resistance contribute to this concerning trend. To combat the spread of gonorrhea, it is crucial to promote safe sex practices, increase awareness about the infection, and develop new treatment strategies to overcome antibiotic resistance. Only through comprehensive efforts can we hope to reverse the epidemiological trends and reduce the burden of gonorrhea on public health.
The Impact Of Gonorrhea On Public Health
Gonorrhea, also known as “the clap,” is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This STI can have a significant impact on public health due to its high transmission rates and potential complications if left untreated. It is essential to raise awareness about the impact of gonorrhea on public health to improve prevention and control strategies.
Gonorrhea is one of the most prevalent STIs globally, affecting millions of individuals each year. The global incidence and prevalence of gonorrhea are alarmingly high, with a significant burden in both developed and developing countries. This STI primarily affects sexually active individuals, especially those engaged in high-risk behaviors such as unprotected sex or having multiple sexual partners.
Several risk factors contribute to the transmission and acquisition of gonorrhea. These include engaging in unprotected sex, having multiple sexual partners, and engaging in high-risk sexual behaviors. certain populations, such as adolescents, men who have sex with men, and individuals with a history of other STIs, are at an increased risk of acquiring gonorrhea.
- Gonorrhea rates among different age groups can vary significantly. While individuals of all ages can be affected by this STI, certain age groups may be particularly vulnerable. Adolescents and young adults are at a higher risk due to factors such as early sexual debut, lack of awareness, and inconsistent condom use. On the other hand, older adults may also be at risk, especially if they engage in risky sexual behaviors.
| Age Group | Gonorrhea Rate |
|---|---|
| Adolescents and young adults | High |
| Adults | Moderate |
| Older adults | Varies |
Gonorrhea prevalence can also vary across different geographical regions. Factors such as cultural norms, access to healthcare, and public health interventions play a crucial role in determining the burden of this STI in specific areas. Developing countries and regions with limited resources often face challenges in implementing effective prevention and control strategies, resulting in higher gonorrhea prevalence rates.
Over the years, the epidemiological trends of gonorrhea have shown fluctuations. Periods of increased incidence and prevalence have been observed, highlighting the need for continuous monitoring and adaptation of public health interventions. New strains of drug-resistant gonorrhea have emerged, posing significant challenges to treatment and control efforts.
The impact of gonorrhea on public health is profound. If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to severe complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women, increased risk of HIV transmission, infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pelvic pain. The economic burden associated with treating and managing gonorrhea and its complications also contributes to the overall impact on public health.
Accurate diagnosis of gonorrhea is crucial for effective management and prevention of further transmission. However, diagnosing gonorrhea accurately can be challenging due to various factors, including asymptomatic infections and limitations in laboratory testing. Improved diagnostic technologies and increased access to testing facilities are necessary to overcome these challenges.
Prevention and treatment of gonorrhea infections are essential for reducing its impact on public health. Strategies include health education and promotion campaigns, promotion of safe sexual practices, availability of affordable and accessible testing facilities, and appropriate use of antibiotics. Timely diagnosis and treatment play a crucial role in preventing complications and further transmission.
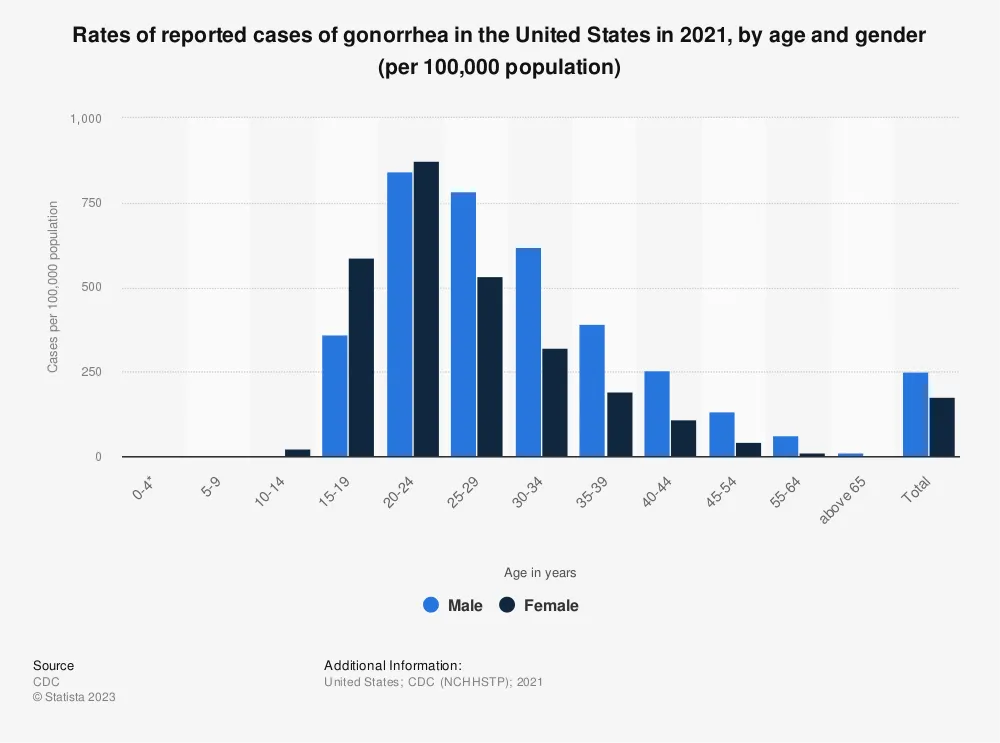
Gonorrhea Rates Among Different Genders
Gonorrhea, also known as “the clap,” is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is one of the most common STIs worldwide, with millions of new cases reported each year. While gonorrhea can affect both males and females, there are significant differences in the rates of infection based on gender.
Among heterosexual individuals, women have a higher risk of contracting gonorrhea compared to men. This can be attributed to biological factors, as the anatomy of the female reproductive system makes it easier for the bacteria to enter and infect the body. certain social and cultural factors play a role in the disparities seen between genders.
- Women:
| Age Group | Gonorrhea Incidence |
|---|---|
| 15-24 | High |
| 25-34 | Moderate |
| 35+ | Low |
In women, the highest rates of gonorrhea infection are typically seen in the younger age group of 15-24. This can be attributed to a combination of factors, including higher rates of sexual activity, lack of knowledge about safe sex practices, and barriers to accessing healthcare. As women age, their risk of gonorrhea decreases but remains a concern.
- Men:
| Age Group | Gonorrhea Incidence |
|---|---|
| 15-24 | Moderate |
| 25-34 | High |
| 35+ | Low |
On the other hand, men tend to have higher rates of gonorrhea infection in the older age group of 25-34. This can be attributed to various factors, including increased sexual activity, higher chances of engaging in unprotected sex, and a lack of awareness about STI prevention among older individuals.
It is important to note that these patterns may vary based on geographic location and other demographic factors. it is crucial for both men and women to practice safe sex, including the use of condoms and regular STI screenings, in order to prevent the spread of gonorrhea and other STIs.
Challenges In Diagnosing Gonorrhea Accurately
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria. It is one of the most common STIs globally, affecting millions of people each year. Diagnosing gonorrhea accurately can be challenging due to several factors.
One of the main challenges in diagnosing gonorrhea accurately is the lack of visible symptoms in many cases. In fact, up to 80% of women and 50% of men infected with gonorrhea do not experience any noticeable symptoms. This makes it difficult for individuals to know whether they are infected and seek appropriate medical care.
Another challenge is the potential for misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. The symptoms of gonorrhea can be similar to other sexually transmitted infections or urinary tract infections. This can lead to misdiagnosis and delay in receiving appropriate treatment. Moreover, healthcare providers may not routinely test for gonorrhea unless a patient specifically requests it or presents with certain symptoms.
- the accuracy of diagnostic tests for gonorrhea can be a challenge. The most common diagnostic methods include nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) and culture tests. While these tests are generally reliable, false negatives and false positives can still occur. False negatives can happen if the test is performed too soon after exposure or if the specimen is not collected correctly. False positives can occur due to laboratory errors or cross-reactivity with other bacteria.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Lack of visible symptoms | Gonorrhea often does not present noticeable symptoms, making it challenging to identify the infection. |
| Misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis | Similar symptoms to other infections can lead to misdiagnosis or delays in receiving appropriate treatment. |
| Inaccurate diagnostic tests | Different factors can contribute to false negatives or false positives in the diagnostic tests for gonorrhea. |
Diagnosing gonorrhea accurately can be a challenging task. The lack of visible symptoms, potential for misdiagnosis, and the possibility of inaccurate diagnostic tests all contribute to these challenges. It is crucial for healthcare providers to stay updated on the latest diagnostic guidelines and for individuals to be proactive in seeking regular STI testing. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential in managing and preventing the spread of gonorrhea.
Preventing And Treating Gonorrhea Infections
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is one of the most common STIs worldwide, with millions of new cases being reported each year. The infection primarily affects the genitals, but it can also spread to other parts of the body such as the rectum, throat, and eyes.
Preventing gonorrhea is crucial in controlling the spread of the infection. The most effective way to prevent gonorrhea is to practice safe sex. This includes using condoms correctly and consistently during vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Condoms act as a barrier, preventing the bacteria from entering the body. It’s important to note that while condoms can significantly reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission, they may not provide complete protection as the infection can also be spread through contact with infected areas not covered by condoms.
In addition to condom use, regular testing and early treatment of gonorrhea infections play a vital role in preventing the spread of the disease. Testing for gonorrhea is relatively simple and can be done through swabs or urine samples. It is recommended that sexually active individuals, especially those with multiple partners or who engage in high-risk sexual behaviors, get tested regularly for gonorrhea and other STIs.
- Adhering to the prescribed treatment regimen is equally important in preventing the spread of gonorrhea. Treatment typically involves a course of antibiotics to kill the bacteria and reduce the risk of complications. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms disappear, to ensure that the infection is fully treated.
- It is crucial to inform sexual partners about the gonorrhea infection to prevent further transmission. All recent sexual partners should be notified so that they can also seek testing and treatment. This is known as partner notification or contact tracing. Partner notification services can help individuals communicate with their partners while maintaining anonymity.
- Moreover, practicing mutual monogamy (being in a sexual relationship with only one partner who is also exclusively sexually active with you) can reduce the risk of contracting gonorrhea and other STIs. It is important to have open and honest conversations with sexual partners about STI testing, previous sexual history, and the use of protection.
Preventing and treating gonorrhea infections require a comprehensive approach that includes safe sex practices, regular testing, early treatment, partner notification, and open communication about sexual health. By taking these preventive measures, individuals can protect themselves and their sexual partners from the transmission and consequences of gonorrhea infections.
| Preventive Measures for Gonorrhea | Treatment of Gonorrhea |
|---|---|
| 1. Safe sex practices: Use condoms correctly and consistently during sexual activity. | 1. Antibiotics: Follow the prescribed course of antibiotics to treat the infection. |
| 2. Regular testing: Get tested for gonorrhea and other STIs regularly, especially if sexually active. | 2. Partner notification: Inform sexual partners about the infection and encourage them to seek testing and treatment. |
| 3. Mutual monogamy: Be in a sexually exclusive relationship with only one partner who is also exclusively sexual with you. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is gonorrhea and how does it spread?
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
What is the global incidence and prevalence of gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections worldwide, with an estimated incidence of around 87 million cases each year. The prevalence varies across different regions and populations.
What are the risk factors for gonorrhea infection?
Risk factors for gonorrhea infection include having multiple sexual partners, engaging in unprotected sex, having a history of sexually transmitted infections, and engaging in high-risk sexual behaviors.
How do gonorrhea rates differ among different age groups?
Gonorrhea rates can vary among different age groups, with higher rates typically observed among young adults aged 15 to 24 years. However, anyone who is sexually active can be at risk of acquiring gonorrhea.
How does gonorrhea prevalence differ in different geographical regions?
Gonorrhea prevalence can vary across different geographical regions due to variations in sexual behaviors, access to healthcare services, and cultural factors. Certain regions may have higher rates of gonorrhea compared to others.
What are the epidemiological trends of gonorrhea over the years?
Gonorrhea has shown a concerning trend of increasing antibiotic resistance over the years, making it more challenging to treat. changes in sexual behavior and healthcare strategies can affect the overall epidemiological trends of gonorrhea.
What is the impact of gonorrhea on public health?
Gonorrhea poses a significant public health concern due to its potential complications and associated health risks. If left untreated, it can lead to serious reproductive health problems, including infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and an increased risk of HIV transmission.
What challenges are faced in accurately diagnosing gonorrhea?
Accurate diagnosis of gonorrhea can be challenging due to the fact that many infected individuals may not show any symptoms. Testing methods and strategies may also vary, and false-negative results can occur. It is crucial to undergo regular sexual health screenings for early detection and treatment.
How can gonorrhea infections be prevented and treated?
Gonorrhea infections can be prevented by practicing safe sex, including the use of condoms, reducing the number of sexual partners, and getting vaccinated if available. Treatment typically involves the use of antibiotic medications prescribed by healthcare professionals. It is essential to complete the full course of treatment as directed.